Assessing the Risks of Token Inflation for Investors and Holders
November 4, 2025
6 mins read
The Inflationary Model is a prominent economic framework within the realm of cryptocurrencies. It involves the continuous printing of tokens over time, without a predetermined limit on their creation.

The Inflationary Model is a prominent economic framework within the realm of cryptocurrencies. It involves the continuous printing of tokens over time, without a predetermined limit on their creation. While various iterations of the model exist, with some tokens imposing annual limits on token creation and others following a predetermined schedule indefinitely, the essence of this model bears a resemblance to fiat currencies. However, what sets it apart is that the token model and issuance are governed by code and a decentralized community, offering greater efficiency and transparency.
I. What is the Inflationary Model?
The Inflationary Model represents an economic system where tokens are continuously printed and circulated within a cryptocurrency ecosystem. Unlike deflationary models or fixed-supply tokens, the Inflationary Model resembles traditional fiat currencies in its approach to token creation. However, the decentralized nature of this model, driven by code and community consensus, enhances its efficiency and transparency.
In this model, there is no capped limit on the total number of tokens that can ever be created. Instead, tokens are printed over time, following specific rules and protocols established by the blockchain network. Some inflationary tokens may limit token creation on an annual basis, while others adhere to a predetermined schedule for token issuance in perpetuity. Regardless of the specific implementation, the key characteristic of the Inflationary Model is the continuous printing of tokens.

II. Features Explaining the Use of the Inflationary Model
Several features contribute to the adoption and utilization of the Inflationary Model in the cryptocurrency space:
-
Familiarity and Viability: The Inflationary Model, resembling fiat currencies, benefits from the extensive study and acceptance of traditional economic systems. Its viability has been demonstrated to a significant extent, reducing doubts regarding its functionality. Economic models that closely resemble existing systems often garner more confidence and attract a wider user base.
-
Continuous Token Supply: One of the notable advantages of the Inflationary Model is the continuous token issuance, which ensures a consistent flow of tokens within the ecosystem. This dynamic nature accommodates growing demands and promotes liquidity and circulation. By avoiding scarcity, inflationary tokens can facilitate transactions and maintain a healthy level of liquidity in the market.
-
Market Incentives: Inflationary tokens can incentivize spending and discourage hoarding, as the ongoing token creation discourages storing tokens for long periods. Unlike deflationary models, where the limited supply encourages users to hoard tokens in anticipation of future value appreciation, inflationary models promote active usage of tokens. This can contribute to a healthy circulation of tokens and prevent the token's devaluation due to a lack of activity.
-
Economic Stability: The Inflationary Model, when properly balanced, can provide a level of economic stability within the cryptocurrency ecosystem. By regulating the rate of token creation and adjusting it based on market conditions, the model can help mitigate extreme price volatility and create a more predictable environment for users and investors.
III. Replaceable Token Models
While the Inflationary Model represents a prominent approach in the cryptocurrency space, alternative token models have emerged to address different economic objectives and challenges. Two notable alternatives include the Deflationary Model and the Duel-Token Model.
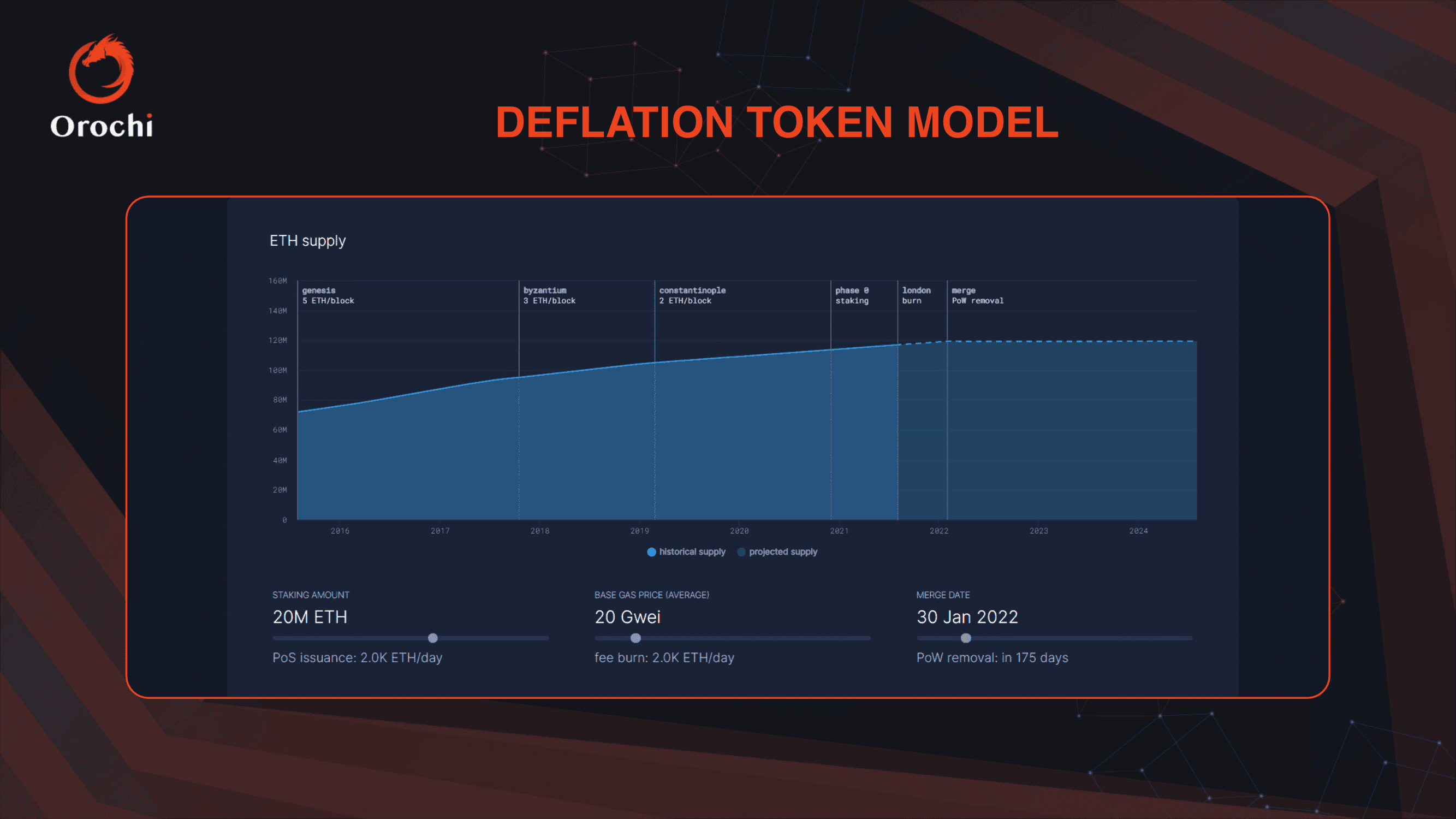
1. Deflationary Model: The Deflationary Model, exemplified by Bitcoin, features a fixed supply of tokens, ensuring scarcity and a potential increase in value over time. In this model, there is a set number of tokens to be created, with that limit never being adjusted upward. This creates a deflationary currency where even as demand increases, supply does not. The limited supply of tokens generates natural demand as the supply dwindles. It also completely eliminates the worry of inflation, which plagues fiat currencies. However, some concerns exist regarding the incentive structure of the deflationary model. Because there is a limit to the number of tokens produced, users are incentivized to hoard tokens rather than spend them. Without enough spending, most tokens will fall out of circulation, leading to decreased liquidity and potential token devaluation.
**2. Duel-Token Model: **The Duel-Token Model involves the use of two distinct tokens within a single blockchain network to create a more robust economic structure. In this model, one token typically functions as a store of value, while the other token serves as a utility token to fuel actions and transactions on the blockchain network. This separation of tokens aims to provide better economic incentives for participants. The store-of-value token can generate returns in the form of the utility token, providing an additional incentive for investors to hold it. By separating financial incentives from utility, the Duel-Token Model attempts to strike a balance between different functions within a blockchain ecosystem. However, the complex nature of this model can make it challenging for the average user to understand and choose between the two tokens, potentially introducing confusion and decision-making difficulties.

IV. How to Prepare to Mitigate the Impact of the Inflationary Model
To navigate the Inflationary Model effectively and avoid potential adverse effects, users should consider the following:
-
Research and Due Diligence: Users should conduct thorough research and understand the fundamentals of any inflationary token they plan to invest in or utilize. This includes examining the token's economic model, the rules governing token creation, and the long-term implications of ongoing token issuance. Understanding these factors can help users make informed decisions and assess the potential risks and rewards associated with the token.
-
Risk Management: It is essential for users to assess and manage the risks associated with inflationary tokens. This involves diversifying one's cryptocurrency portfolio, setting appropriate investment thresholds, and adopting risk management strategies to mitigate potential token devaluation risks. By diversifying investments and managing exposure to inflationary tokens, users can reduce the impact of any potential adverse market conditions.
-
Monitoring Market Conditions: Staying informed about market trends, inflation rates, and the overall health of the token ecosystem is crucial. Monitoring these factors can help users make informed decisions, adjust their investment strategies, and take advantage of opportunities or mitigate risks as they arise.
By implementing these measures, users can better position themselves to navigate the Inflationary Model and mitigate potential risks associated with ongoing token creation.
Conclusion
The Inflationary Model represents a distinctive token model within the cryptocurrency landscape, characterized by continuous token creation without a predefined limit. While it shares similarities with fiat currencies, its decentralized nature offers enhanced efficiency and transparency. Understanding the features and considerations associated with the Inflationary Model, as well as alternative token models, empowers users to navigate the cryptocurrency space effectively and make informed decisions regarding their investments and participation. Through research, risk management, and market monitoring, users can prepare themselves to harness the benefits of the Inflationary Model while mitigating potential risks.
Experience verifiable data in action - Join the zkDatabase live demo!
Book a Demo











